Difference between revisions of "Cattaskv2009 Communication"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Rhino Service Bus == | == Rhino Service Bus == | ||
| − | [http://ayende.com/Blog/archive/2008/12/17/rhino-service-bus.aspx Rhino Service Bus] (RSB) is an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_service_bus ESB] which is built on the top of MSMQ. In short, a Rhino service bus: | + | [http://ayende.com/Blog/archive/2008/12/17/rhino-service-bus.aspx Rhino Service Bus] (RSB) is an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_service_bus ESB] which is built on the top of MSMQ. Since the bus behaviours are mainly specified by its configuration file, we'd better look at the configuration to learn how the bus works: |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <facility id="rhino.esb" ><br> <bus threadCount="1" numberOfRetries="5" endpoint="msmq://localhost/starbucks.customer" /><br> <messages><br> <add name="CatGlobe.Messages.WebShop" endpoint="msmq://web/WebShop"/><br> <add name="CatGlobe.Messages.CatTask" endpoint="msmq://catmaxb/CatTask"/><br> </messages><br></facility><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In short, a Rhino service bus: | ||
[[Image:CatTask A simple bus.JPG]] | [[Image:CatTask A simple bus.JPG]] | ||
| − | + | *Has a queue which it monitors for incoming messages. It is the "own queue" in the image below. When messages come, the bus will receive the messages from the queue and invoke the appropriate consumers to process the them. For instance: in the image below, we have a consumer called CatGlobeMessageController which implements the IConsumerOf<HelloCatGlobe> interface. When messages of the type come, the bus will invoke CatGlobeMessageController to process them. | |
[[Image:CatTask A simple consumer.JPG]] | [[Image:CatTask A simple consumer.JPG]] | ||
| − | - | + | *Can send messages to other queues (of course!!!). The point here is that it has two Send APIs: |
| + | |||
| + | - Send with an explicitly specified end point (queue). | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Send without a specified endpoint. We need to specify the queues (message owners) of | ||
| + | |||
| + | * | ||
== Buses design for CatTask == | == Buses design for CatTask == | ||
Revision as of 03:56, 20 March 2009
Contents
Communication in Cattask v2009
What kind of communication do we need?
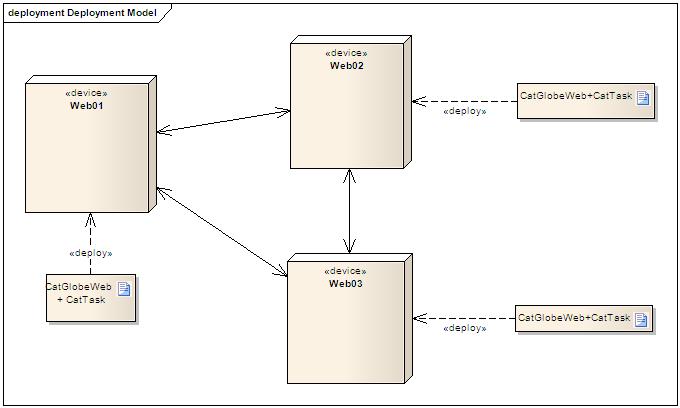
In the real production environment, because of the use of network balancing, one CatGlobe site is deployed in three separate servers. Besides, we decided that there will be one "Cattask" for one deployed instance of a site. The running production environment should look like:
The problem is that the three cattasks won't run independently. Instead, they must contact with each others to share information about scheduled tasks, tasks execution...
So what communication technology should we use?
We have investigated 3 communication techniques so far: remoting, WCF and MSMQ. You can find the whole story here Remoting,WCF and MSMQ for CatTask . At the moment, we are designing the module using MSMQ with the help of Rhino Service Bus.
Rhino Service Bus
Rhino Service Bus (RSB) is an ESB which is built on the top of MSMQ. Since the bus behaviours are mainly specified by its configuration file, we'd better look at the configuration to learn how the bus works:
<facility id="rhino.esb" >
<bus threadCount="1" numberOfRetries="5" endpoint="msmq://localhost/starbucks.customer" />
<messages>
<add name="CatGlobe.Messages.WebShop" endpoint="msmq://web/WebShop"/>
<add name="CatGlobe.Messages.CatTask" endpoint="msmq://catmaxb/CatTask"/>
</messages>
</facility>
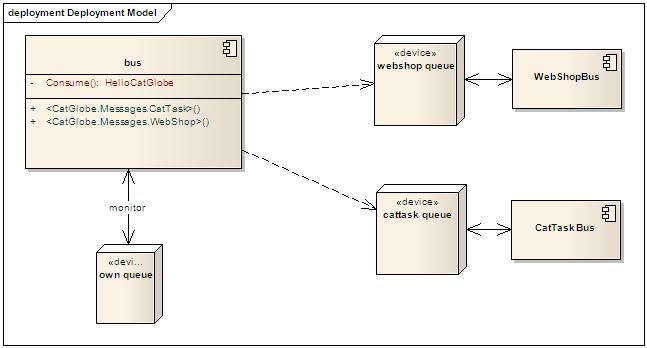
In short, a Rhino service bus:
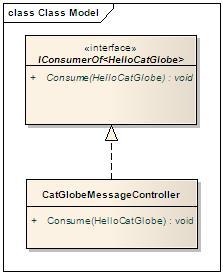
- Has a queue which it monitors for incoming messages. It is the "own queue" in the image below. When messages come, the bus will receive the messages from the queue and invoke the appropriate consumers to process the them. For instance: in the image below, we have a consumer called CatGlobeMessageController which implements the IConsumerOf<HelloCatGlobe> interface. When messages of the type come, the bus will invoke CatGlobeMessageController to process them.
- Can send messages to other queues (of course!!!). The point here is that it has two Send APIs:
- Send with an explicitly specified end point (queue).
- Send without a specified endpoint. We need to specify the queues (message owners) of