Difference between revisions of "Cattaskv2009 Communication"
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
=== Buses configuration === | === Buses configuration === | ||
| − | == Use cases == | + | == Use cases == |
| + | |||
| + | === Subcriptions === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Looking for Controller's endpoint === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Controller election === | ||
Revision as of 07:29, 25 March 2009
Contents
Communication in Cattask v2009
The new CatTask model which was discussed in Cattaskv2009_overview_of_the_new_system shows that there will be a lot of communication among the 3 CatTask instances. Besides, experience in working with the current CatTaskService tells me that this is the most error-prone part in production environment. Those can explain why we have spent so much attention on building a good communication component.
So what communication technology should we use?
We have investigated 3 communication techniques so far: remoting, WCF and MSMQ. Besides, we found some interesting tricks. You can find the whole story in Remoting,WCF and MSMQ for CatTask.
At the moment, we are designing the module using MSMQ with the help of Rhino Service Bus.
Rhino Service Bus
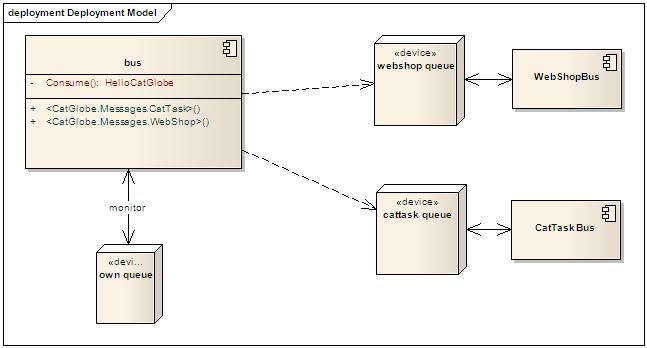
Rhino Service Bus (RSB) is an ESB which is built on the top of MSMQ. Since the bus behaviours are mainly specified by its configuration file, we'd better look at the configuration to learn how the bus works:
<facility id="rhino.esb" >
<bus threadCount="1" numberOfRetries="5" endpoint="msmq://localhost/ownqueue" />
<messages>
<add name="CatGlobe.Messages.WebShop" endpoint="msmq://web/WebShop"/>
<add name="CatGlobe.Messages.CatTask" endpoint="msmq://catmaxb/CatTask"/>
</messages>
</facility>
In short, a Rhino service bus:
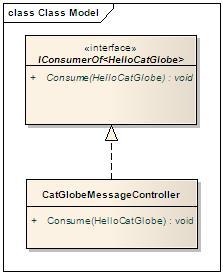
- In the <bus> element we can see an end point. It is the queue which the bus monitors for incoming messages. When messages come, the bus receive messages from the queue and invoke the appropriate consumers to process them. For example: in the image below, we have a consumer called CatGlobeMessageController which implements the IConsumerOf<HelloCatGlobe> interface. When messages of the type come, the bus invokes CatGlobeMessageController to process them.
- Can send messages to other queues (of course!!!). The point here is that it has two Send APIs:
- Send with an explicitly specified end point (queue).
- Send without a specified endpoint. We need to specify the queues (message owners) of the message type. Notice the <messages> section in the configuration block above: it says that all the messages of types which are defined in the CatGlobe.Messages.WebShop namespace will be sent to the "msmq://web/WebShop" end point. So is the second setting for CatTask.
- Publish/Notify: another feature of RSB is the ability to publish/notify messages to all the buses who are interested in. In order to receive published messages, a consumer must subscribe itself to the producer bus. For example, a bus can subscribe to the CatTask bus that it is interested in messages of the type CatGlobe.Messages.CatTask.TaskCompleted. After the subcription is done, whenever the CatTask bus publishes a TaskCompleted message, one will be sent to the subscriber bus.
Should we use RSB?
At the moment, my answer is YES. Let's consider pros and cons of it:
- Pros:
- It was made and is being contributed by many good developers, well unittested.
- It solves many issues which I ran into when I tried to write my own MSMQ code. Well, I'm not a giant, but I can stand on the shoulder of giants.
- The built-in logger is very good. It can help us figure out any problem easily.
- Cons:
- RSB is used in the distributed contexts where there may be a delay time between when a message is sent and when it is received. The problem will be raised in the next section.
- The help file is not good. Yeah, as I just said, we can stand on the shoulder of giants, but we have to start from the ground and there is no stairs for us to climb to the shoulder! (On the contrary, with Microsoft framework, we often have more than one stairs to use, but some of them have a gap in the middle and some others lead you to a dead-end!!!)
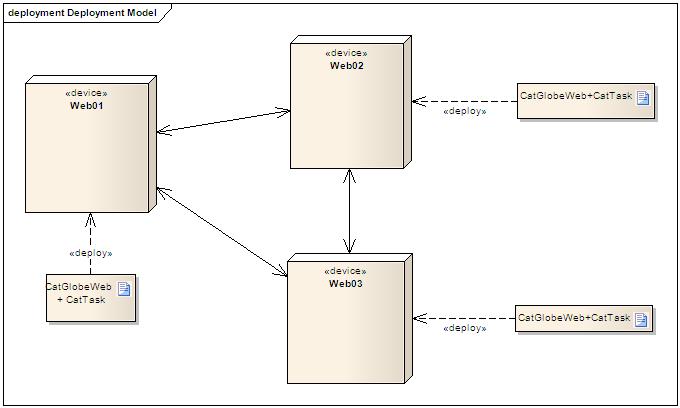
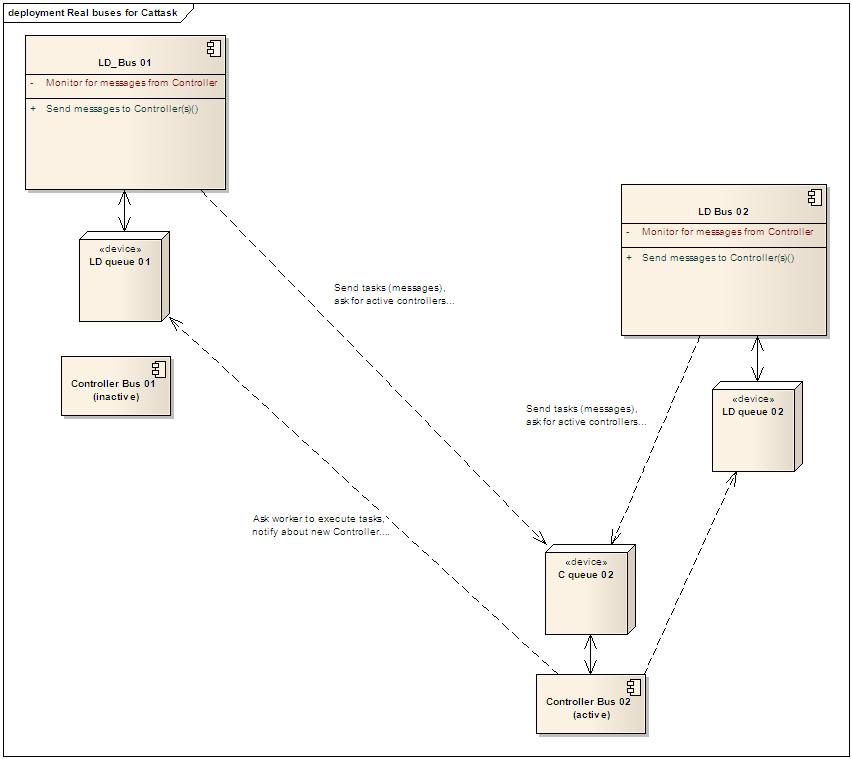
Buses design for CatTask
- We are using the option #3 for Controller.
- The real implementation may vary a little bit: it is possible to use one queue for both LD and Controller. We will decide it later. In this design, we will use one queue for each. In my opinion, it may help us understand the system more easily.
Buses diagram
- A CatTask instance has two buses:
- One, which is LD_Bus in the image below, for the local part of it: LD and Worker.
- The another is Controller_Bus which is used for the Controller.
Message namespaces
- CatTask.Messages.LocalDispatcher
- CatTask.Messages.Worker
- CatTask.Messages.Controller